
- hasivo@hasivo.com
- Mon - Sat at 7:00AM to 9:00PM
Leave Your Message

In the heart of modern networking, where seamless connectivity and efficient data transfer are paramount, the role of a Network Switch cannot be overstated. A Network Switch serves as a pivotal device that bridges multiple devices within a network, facilitating communication and data sharing among them. As technology evolves and the demands for higher speed and increased bandwidth continue to rise, understanding how a Network Switch operates becomes essential for both IT professionals and everyday users alike.
Industry expert John Smith, a renowned network engineer, emphasizes the significance of this technology: "A Network Switch is not just a device; it’s the backbone of our digital communication." His insight highlights how a Network Switch enables devices to talk to one another more effectively, thereby optimizing network performance and enhancing user experience.
As we delve into the intricacies of network infrastructure, it becomes clear that grasping the fundamentals of a Network Switch and its functionality is vital for anyone looking to navigate the complexities of modern networks. This article aims to explore the essential characteristics of Network Switches, their operational principles, and their impact on today's digital landscape.

A network switch is a crucial device in modern networking that connects various devices within a local area network (LAN), enabling them to communicate with one another efficiently. Unlike a hub, which broadcasts data to all connected devices, a switch intelligently forwards data only to the intended recipient. This capability significantly reduces network congestion and improves overall performance, making switches an essential component in both home and enterprise environments.
Switches operate at the data link layer of the OSI model, using MAC addresses to determine where to send data packets. When a device sends data through the network, the switch examines the destination MAC address and sends the data specifically to that device. This targeted approach allows for simultaneous data transmissions between multiple devices, enhancing network speed and reliability. Additionally, many modern switches offer features like Quality of Service (QoS), VLAN support, and link aggregation, providing more advanced management options to optimize network functionality and security.
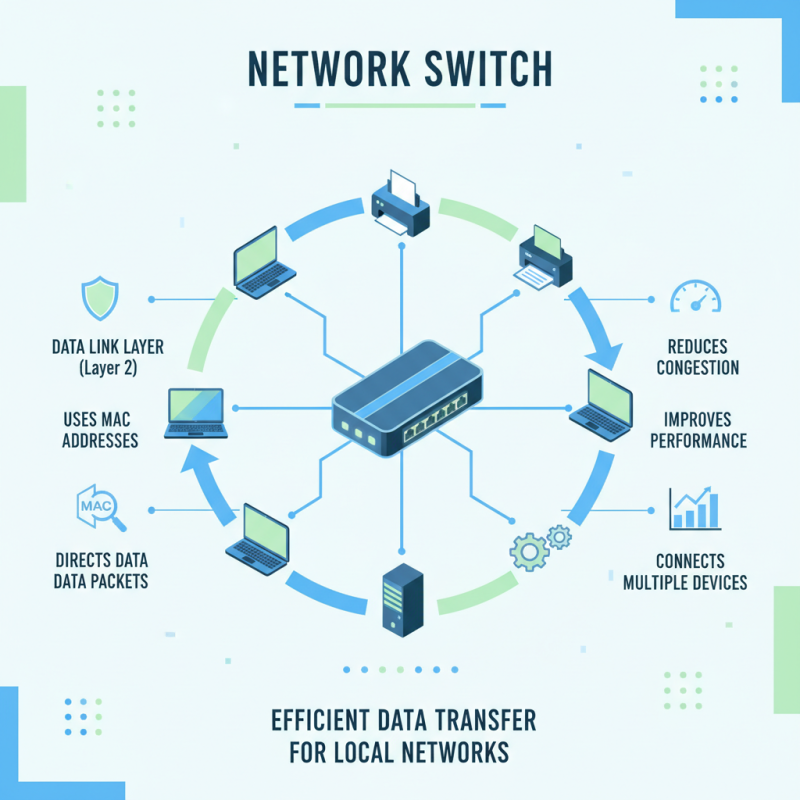
A network switch is a pivotal device in modern networks, facilitating the efficient transfer of data between devices. It operates at the data link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model, enabling multiple devices to connect and communicate within a local area network (LAN). By using MAC addresses, a network switch can accurately direct data packets to their intended destinations, reducing network congestion and improving overall performance. This functionality helps in creating a structured environment where devices, such as computers and printers, can share resources without interfering with each other's operations.
When implementing a network switch in your setup, consider optimizing your network layout to enhance performance. For instance, separating different types of traffic, such as voice, video, and data, can help maintain clarity and speed. This segmentation can be achieved through Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs), which allow you to manage traffic effectively while improving security.
Tips for maintaining your network switch include regular monitoring of network performance and utilization. Keeping an eye on traffic patterns can help you identify bottlenecks or unused resources. Additionally, ensure that your switch's firmware is up-to-date, as updates can introduce performance improvements and security enhancements, keeping your network functioning efficiently in a dynamic environment.
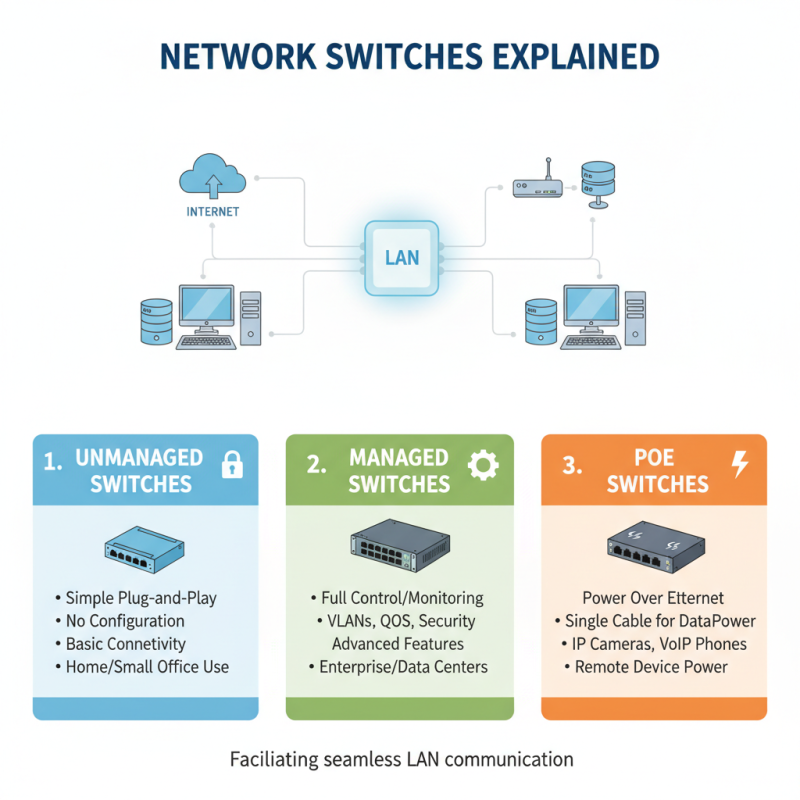
Network switches are pivotal devices in modern networking, facilitating the seamless communication between various devices within a local area network (LAN). There are several types of network switches, each with distinct functionalities and applications, making them suitable for specific networking environments.
The most commonly used types include unmanaged, managed, smart, and layer 3 switches. Unmanaged switches are ideal for small networks where basic plug-and-play functionality suffices, while managed switches provide advanced features like traffic monitoring and VLAN support, catering to larger, more complex environments. According to industry research by Gartner, the managed switch market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.1% from 2021 to 2026, highlighting the increasing demand for more sophisticated networking solutions. Smart switches sit between these two types, offering a balance of configurability and ease of use, making them suitable for small to medium-sized enterprises.
Layer 3 switches, on the other hand, combine the functionality of switches and routers, enabling inter-VLAN routing, which is crucial for modern networks that require efficient data traffic management. These switches are often employed in enterprise environments where scalability and performance are paramount. A study by IDC indicated that organizations implementing layer 3 switching can improve their overall network performance by up to 40%, illustrating their significance in high-capacity networking scenarios. Each type of switch plays a vital role in optimizing network efficiency, adaptability, and performance, catering to various operational needs across different sectors.
In modern networks, the role of
MAC addresses is fundamental to the functionality of network switches.
A Media Access Control (MAC) address is a unique identifier assigned to network interfaces for communications on the physical network segment.
Each device on a local area network (LAN) possesses a distinct MAC address, which enables switches to efficiently direct data packets.
When a switch receives a data frame, it examines the MAC address contained within the frame to determine the intended recipient.
This process allows the switch to forward the frame only to the relevant device, minimizing unnecessary traffic
and enhancing network performance.
Switches maintain a
MAC address table, which stores the relationships between MAC addresses and the corresponding switch ports.
As frames traverse the switch, it learns the source MAC addresses of incoming frames and associates them with the port through which they arrive.
Over time, the switch builds a comprehensive picture of the network's topology. This knowledge allows for rapid delivery of frames to the correct destination,
making communication among devices more efficient. Additionally, the use of MAC addresses plays a crucial role in preventing data collisions
by ensuring that each frame is directed solely to its intended recipient.
This capability is particularly vital in maintaining the speed and reliability of modern network operations.
In modern networks, network switches play a vital role in enhancing both performance and security. By efficiently managing data traffic, switches reduce latency and bottlenecks. According to a report from the International Data Corporation (IDC), nearly 80% of network downtime can be attributed to issues related to insufficient bandwidth and poor device management. Switches optimize traffic by directing data packets only to their intended recipients, which not only speeds up communication but also improves the overall efficiency of the network.
Moreover, network switches contribute significantly to security. As organizations increasingly adopt advanced security protocols, the functionality of switches has evolved to include features like Virtual LANs (VLANs) and Access Control Lists (ACLs). These features allow administrators to segment network traffic, diminishing the risk of unauthorized access and enhancing monitoring capabilities. A study by Forrester Research highlights that organizations leveraging smart switches to implement network segmentation experience a reduction in breach impacts by up to 50%. This dynamic security capability illustrates how network switches are essential for safeguarding sensitive information while maintaining fluid network operation.
| Feature | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Data Packet Filtering | Network switches analyze incoming data packets and forward them to the specific device on the network. | Increases bandwidth by reducing unnecessary data transmission across the network. |
| Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) Support | Allows network administrators to segment a physical network into multiple logical networks. | Enhances security and performance by segregating traffic types. |
| Traffic Management | Switches can prioritize data packets based on the type of application. | Improved performance for critical applications through Quality of Service (QoS) mechanisms. |
| Redundancy and Reliability | Many modern switches support protocols like Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to prevent loops. | Minimizes downtime and ensures continuous network availability. |
| Security Features | Includes features like port security and network access control. | Protects against unauthorized access and enhances data security. |





